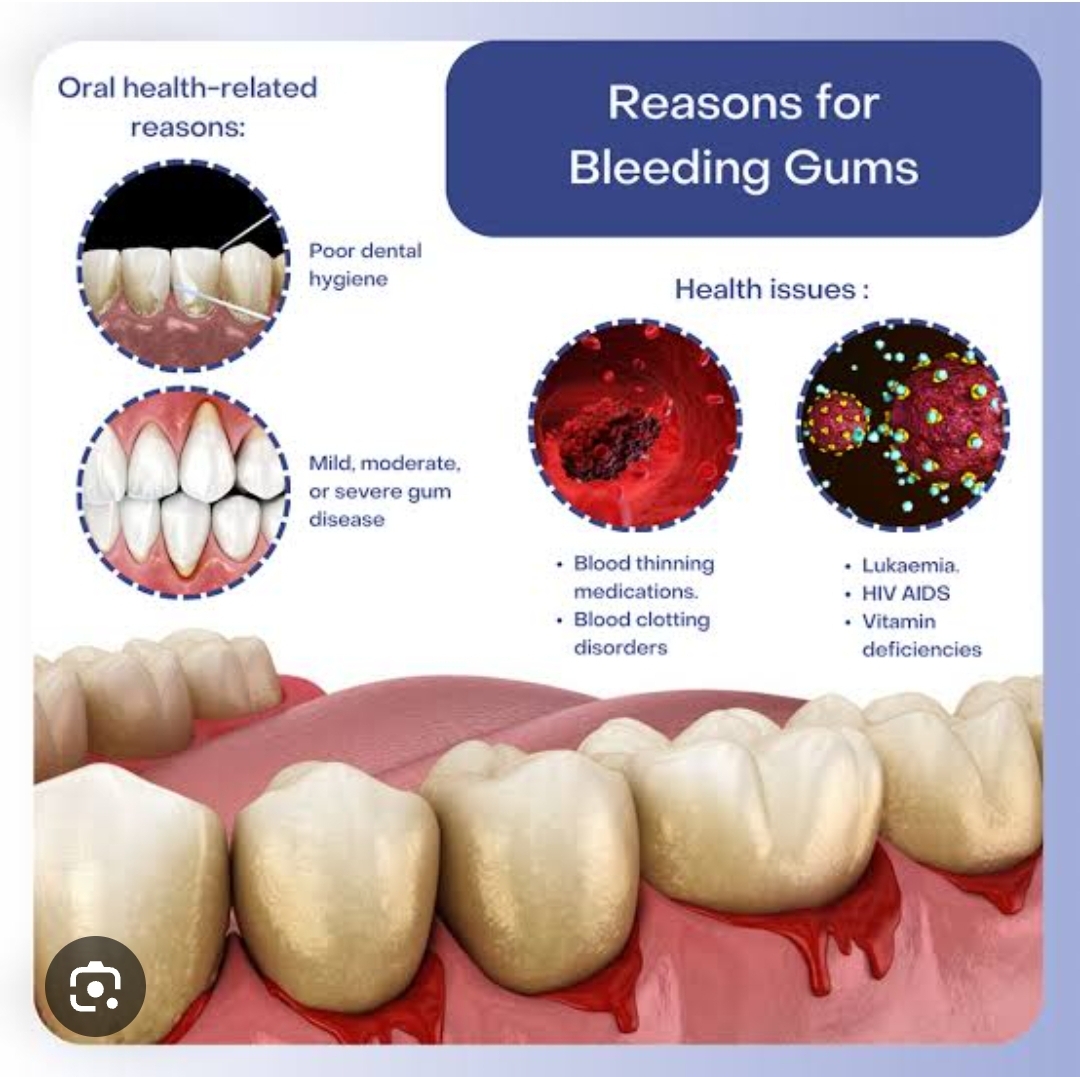
Gum bleeding can have several causes, ranging from mild irritation to more serious underlying conditions. Here are the most common causes:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Plaque buildup leads to gingivitis (early-stage gum disease), causing red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
Not brushing or flossing properly allows bacteria to irritate the gums.
2. Gingivitis
The most common cause of bleeding gums.
Caused by plaque buildup along the gumline.
Symptoms: swollen, tender, and bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing.
3. Periodontitis (Advanced Gum Disease)
A progression from untreated gingivitis.
Involves inflammation and infection of the deeper tissues and bones supporting teeth.
Gums may bleed, recede, and teeth may become loose.
4. Aggressive Brushing or Flossing
Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing too hard can damage gum tissue.
Improper flossing technique can also irritate gums and cause bleeding.
5. Vitamin Deficiencies
Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy): causes weakened gum tissue and bleeding.
Vitamin K deficiency: affects blood clotting and can lead to bleeding.
6. Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
7. Medications
Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin, aspirin) can increase the likelihood of bleeding.
Some medications cause dry mouth, which may lead to gum problems.
8. Medical Conditions
Diabetes: increases risk of gum disease.
Leukemia: bleeding gums can be an early sign.
Bleeding disorders: like hemophilia or thrombocytopenia.
9. Tobacco Use
Smoking and other forms of tobacco can harm gums and mask symptoms like bleeding until damage is advanced.
10. Ill-Fitting Dental Appliances
Dentures or braces that don’t fit properly can rub against the gums and cause irritation and bleeding.