Measles is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the measles virus (a paramyxovirus). It spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Here’s a clear, useful overview:
Key Facts
Transmission: Extremely contagious; up to 90% of unvaccinated people close to an infected person may become infected.
Incubation period: ~10–14 days after exposure.
Contagious period: From 4 days before to 4 days after the rash appears.
Symptoms
Measles typically progresses in stages:
1. Early symptoms (3–4 days)
High fever
Cough
Runny nose
Red, watery eyes (conjunctivitis)
Koplik spots: tiny white spots inside the cheeks—classic sign before the rash.
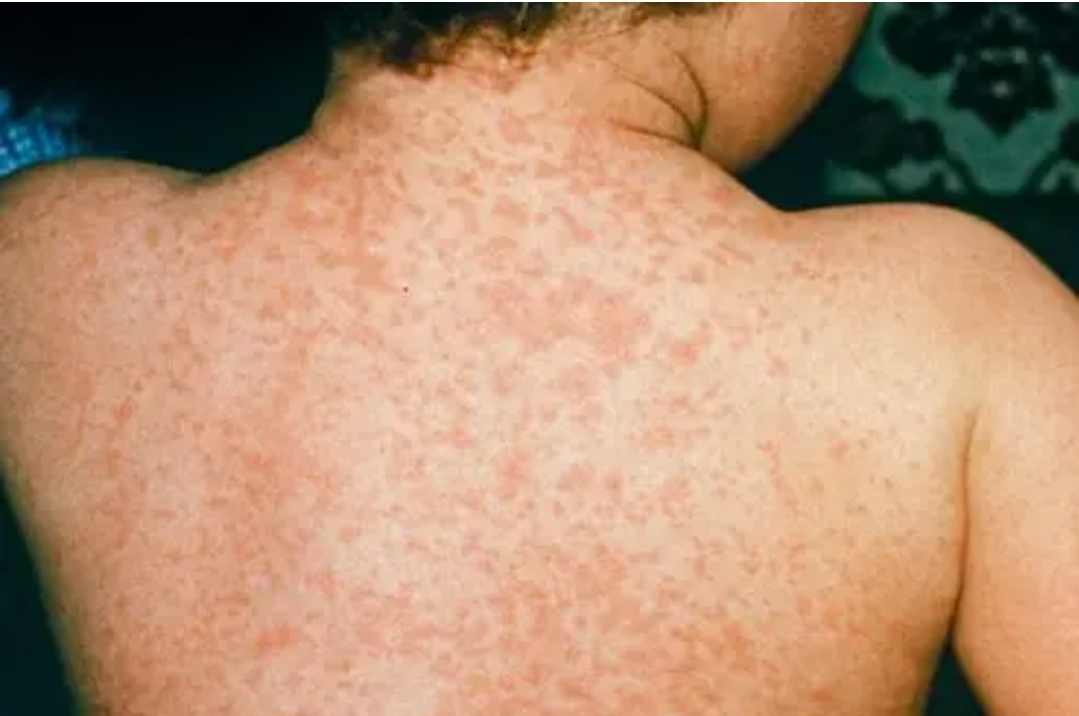
2. Rash
Begins as flat red spots on the face/hairline.
Spreads downward to the trunk, then limbs.
May merge into patches.
Fever can spike to 104°F (40°C) when the rash appears.
Complications
Measles can be serious, especially for:
young children
pregnant people
immunocompromised individuals
Possible complications:
Ear infections
Severe diarrhea/dehydration
Pneumonia
Encephalitis (brain swelling)
Death (rare but possible)
Prevention
MMR Vaccine
The most effective prevention.
Two-dose schedule:
1st dose: 9 months
2nd dose: 15 months
3rd dose: 4 - 6 years
Protection rate: ~97% after two doses.




