An allergy in children is a reaction of the immune system to a substance (called an allergen) that is normally harmless. When a child with an allergy is exposed to that allergen, their body mistakenly sees it as a threat and responds with symptoms that can affect the skin, breathing, digestion, or more.
🌿 Common Allergens for Children:
Foods – e.g., milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, fish, shellfish
Environmental – pollen, dust mites, mold, pet dander
Insect stings – bees, wasps
Medications – antibiotics like penicillin
Others – latex, certain chemicals in soaps or detergents
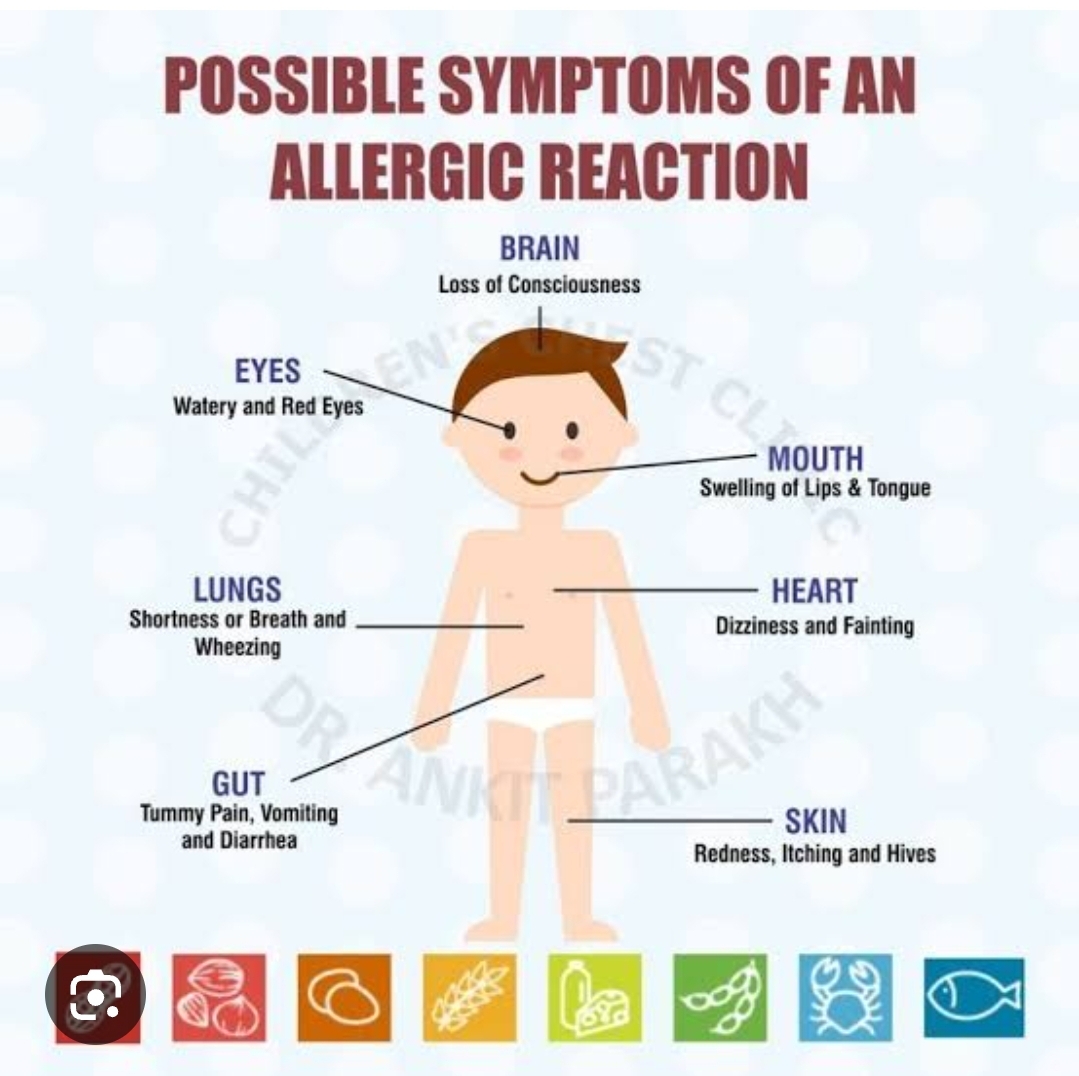
🚨 Common Allergy Symptoms in Children:
Symptoms depend on the type of allergy and can range from mild to severe.
Skin:
Hives (red, itchy welts)
Eczema (dry, scaly patches)
Swelling, especially around the face, lips, or eyes
Respiratory:
Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose
Coughing, wheezing
Shortness of breath
Asthma symptoms
Digestive:
Stomach pain
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Severe Reaction (Anaphylaxis):
Trouble breathing
Swelling of the throat or tongue
Drop in blood pressure
Loss of consciousness
Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency. Children with severe allergies often carry an epinephrine auto-injector (like EpiPen).
🧪 Diagnosis:
If a child shows signs of allergies, a doctor may recommend:
Skin prick tests
Blood tests
Elimination diets (for food allergies)
💡 Treatment and Management:
Avoidance of known allergens
Antihistamines for mild symptoms
Inhalers for asthma-type reactions
Epinephrine for severe reactions
Allergy shots (immunotherapy) in some cases