Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It primarily affects the nose, throat, and lungs and can range in severity from mild to severe.
🔬 Causes
There are four main types of influenza viruses:
Influenza A: Can infect humans and animals; responsible for most flu pandemics.
Influenza B: Only infects humans; generally causes seasonal epidemics.
Influenza C: Causes mild illness; not responsible for epidemics.
Influenza D: Primarily affects cattle; not known to infect humans.
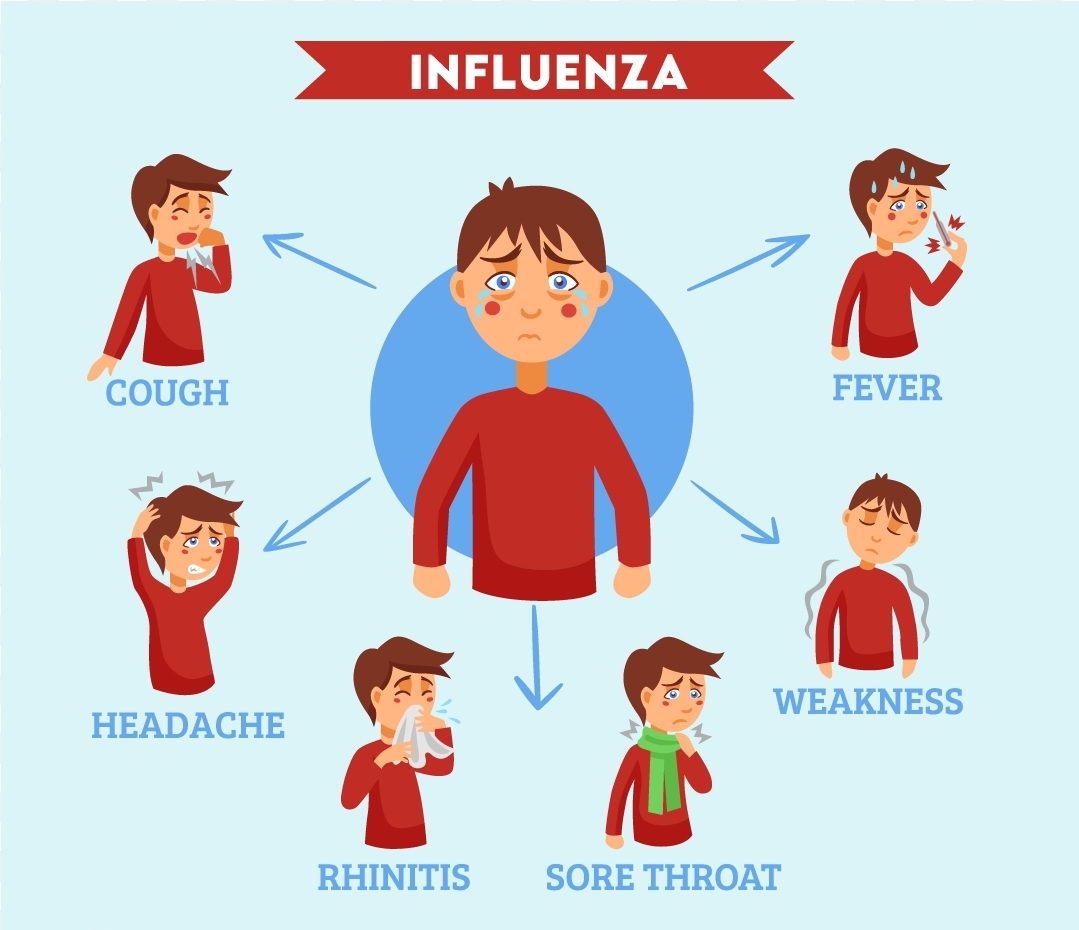
🤒 Symptoms
Symptoms usually appear 1–4 days after infection and can include:
High fever or chills
Cough
Sore throat
Runny or stuffy nose
Muscle or body aches
Headache
Fatigue (tiredness)
Vomiting and diarrhea (more common in children)
🧫 Transmission
Influenza spreads mainly through:
Airborne droplets from coughing, sneezing, or talking.
Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the mouth, eyes, or nose.
👥 Who’s at Risk?
High-risk groups for severe complications:
Young children
Elderly adults (65+)
Pregnant women
People with chronic health conditions (e.g., asthma, diabetes, heart disease)
Immunocompromised individuals
💉 Prevention
Annual flu vaccine: Best way to prevent the flu.
Frequent handwashing
Avoiding close contact with sick people
Covering coughs and sneezes
Staying home when sick