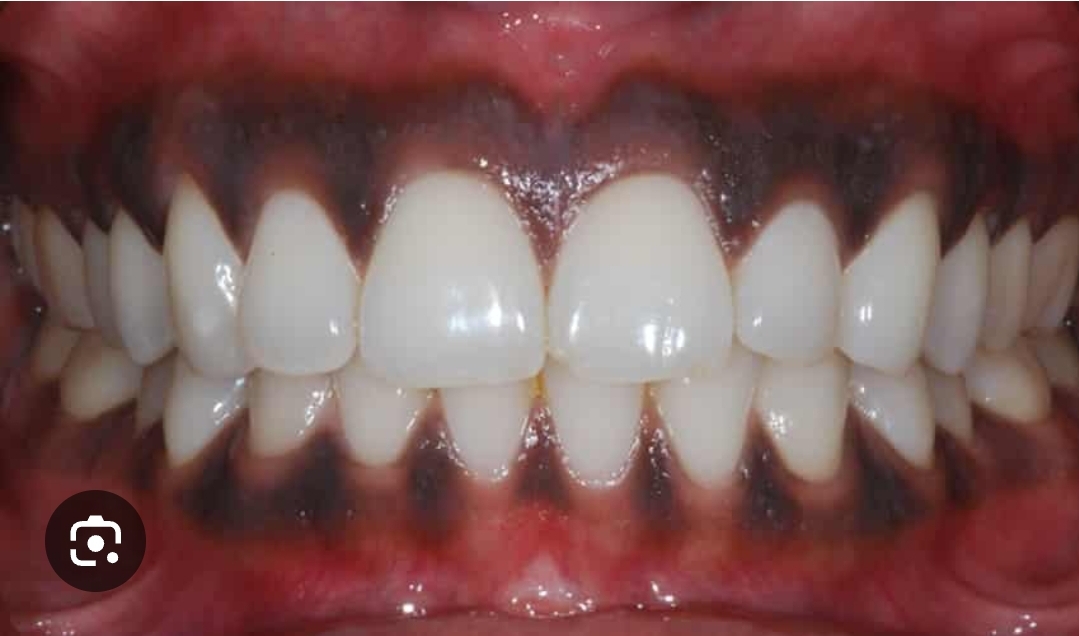
Gums can turn dark (brown, purplish, or blackish) for a number of harmless or medical reasons. Here are the most common:
1. Natural Pigmentation
Many people—especially those with darker skin tones—naturally have more melanin in their gums.
This causes brown or dark patches that are completely normal.
2. Smoking
Nicotine can stimulate melanin production in the gums, known as smoker’s melanosis.
Dark spots usually fade if you stop smoking.
3. Medication Side Effects
Certain medications can cause hyperpigmentation of the gums, including:
Some antimalarials
Minocycline (an antibiotic)
Hormonal medications
Chemotherapy drugs
4. Amalgam Tattoo
A small bluish-gray spot caused by dental filling material (amalgam) embedding in the gum.
Harmless but permanent unless removed.
5. Gum Disease
Inflammation or infection (gingivitis / periodontitis) can cause gums to appear darker or red-purple.
Usually accompanied by bleeding, swelling, or tenderness.
6. Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, puberty, or hormonal therapies can increase melanin and darken gums.
7. Addison’s Disease or Other Medical Conditions
Rare endocrine disorders (like adrenal insufficiency) can cause darkening of gums and other mucous membranes.




